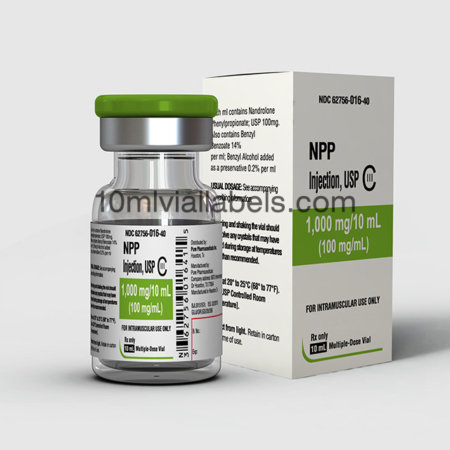
What is the NPP?
NPP, or Nandrolone Phenylpropionate, is an anabolic steroid that is sometimes used for various medical conditions, such as muscle-wasting diseases and anemia. It’s also used by some athletes and bodybuilders to enhance muscle growth and performance, although such use is often illegal and can have serious health risks.
If you’re considering using NPP injections for any purpose, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide guidance based on your specific medical needs or fitness goals. Steroid use should always be done under medical supervision to minimize potential risks and side effects.
The dosage and frequency of NPP injections can vary depending on the individual and the intended purpose. Only a qualified healthcare provider can determine the appropriate dose for your situation and monitor your progress to ensure your safety.
It’s important to note that the misuse of steroids, including NPP, can lead to a range of adverse effects, including hormonal imbalances, cardiovascular issues, liver problems, and psychological side effects. Moreover, using steroids without a prescription is illegal in many countries.
Please consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance regarding the use of NPP injections or any other medical treatments.

What content is necessary on custom brand steroids packaging?
Medicine packaging should include essential information to ensure the safe and effective use of the medication. Here’s a list of key content that should be included:
Medication Name: Clearly state the name of the medication, including both the brand name and generic name (if applicable).
Dosage Strength: Specify the strength or concentration of the medication per unit (e.g., mg, mL, etc.).
Active Ingredients: List the active ingredients along with their quantities per dose.
Dosage Instructions: Provide clear and concise instructions on how to take the medication, including the recommended dosage, frequency, and any special instructions (e.g., with or without food).
Indications: Explain the conditions or symptoms the medication is intended to treat.
Contraindications: Highlight any situations or conditions where the medication should not be used.
Warnings: Include important safety information, such as potential side effects, interactions with other drugs, and precautions to take while using the medication.
Storage Instructions: Specify the recommended storage conditions, such as temperature and humidity requirements.
Expiration Date: Display the date until which the medication is expected to remain effective and safe to use.

Lot or Batch Number: Provide a unique identifier for the specific batch or lot of the medication.
Manufacturer Information: Include the name and contact information of the pharmaceutical manufacturer or distributor.
Barcode/QR Code: Incorporate a barcode or QR code for easy tracking and verification of the product.
Additional Information: Depending on the medication, you may need to include other relevant information, such as special handling instructions, reconstitution instructions (for powders or liquids), or administration devices (if applicable).
Patient Information Leaflet (PIL): In many countries, it’s required to include a patient information leaflet inside the packaging. This leaflet provides more detailed information about the medication, including potential side effects, precautions, and what to do in case of an overdose.
Prescription Label (if applicable): If the medication requires a prescription, the packaging should include a label with the prescribing healthcare provider’s information, patient’s name, and instructions specific to that prescription.

Language and Accessibility: Ensure that the packaging includes information in a language understood by the intended user. In some regions, multiple languages may be necessary to accommodate a diverse population.
Braille and Accessibility Features: Consider adding Braille or other accessibility features to assist visually impaired users.
Child-Resistant Packaging: When required by regulations, ensure that the packaging is child-resistant to prevent accidental ingestion by children.
Dispensing Information: For healthcare professionals, provide any necessary information related to dispensing the medication, such as dosage calculation for different age groups or patient populations.
Remember that specific regulations and requirements for medicine packaging may vary from country to country, so it’s important to adhere to local laws and guidelines when designing packaging for pharmaceutical products. Additionally, consulting with regulatory experts or authorities is advisable to ensure compliance with all necessary standards and regulations.
Order Process

Payment

Logistics and Transportation




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.